Some Ini File Problems That I've
Encountered
My system
Tigerdirect cheapo tower and board - S3
chipset.
Cyrix pr300 - 233 actual
64M ram memory
Mandrake 7.0
Rtlinux-2.0 prepatched
emc-05-May-2000.tgz download and
install (a problem with emcsh compile)
Email me
for my work arounds on these.
Throughout this page I will use dark
green letters to indicate
the lines of text that I entered into
the console (konsole). I will use dark
red to indicate the response of
the computer to my command. Medium
red lines are the focus on the
discussion. For the sake of
brevity, I have edited many of the
responses of the computer when it was
asked to compile large numbers of
files. Some of these lengthy
responses are included as files
and are linked to this document so
that you can compare your results.
So far, I have loaded Mandrake 7.0 on
my clean hard drive. I have built a real
time kernel, and I have successfully
installed EMC. Now I am ready to try
running EMC. So I enter the following
two lines.
[root@localhost
/root]# cd
/usr/local/nist/emc
[root@localhost
emc]# ./emc.run
Current
platform is linux_2_2_13
Current
real-time platform is rtlinux_2_0
inivar
= plat/linux_2_2_13/bin/inivar
INIFILE
= emc.ini
starting
emc...
starting
steppermod.o...plat/rtlinux_2_0/lib/steppermod.o:
invalid parameter PERIODcan't install
it
That's just a little disappointing but I
learned several things. The startup file
found my realtime and nonrealtime
directories and made links to
them. It found and is using
emc.ini . It tried to start emc
using steppermod.o. But it had a
problem with a parameter (variable)
named PERIOD so it quit.
Looking down in the emc.ini file, I
find:
;
Base task period, in seconds
PERIOD
= 0.000016
From experience I know that steppermod
will not run with period defined in the
ini file. I have two choices, change the
steppermod.o to freqmod.o or remove the
period variable. For this try I'm going
to keep steppermod.o because It won't
make my computer work quite as hard. So
I comment out period in emc.ini and save
the file. Comment is a (;) at the start
of a line. (I have since found a bug in
the compile of steppermod.o from the
June 2000 release that does some goofy
stuff to the ini file when you shut down
EMC)
;
Base task period, in seconds
;
PERIOD = 0.000016
I return to the console and press the up
arrow and get:
[root@localhost
emc]# ./emc.run
I press enter and this is the reply.
Current
platform is linux_2_2_13
Current
real-time platform is rtlinux_2_0
inivar
= plat/linux_2_2_13/bin/inivar
INIFILE
= emc.ini
starting
emc...
starting
steppermod.o...done
starting
bridgeportio...done
starting
bridgeporttask...done
running
xemc...
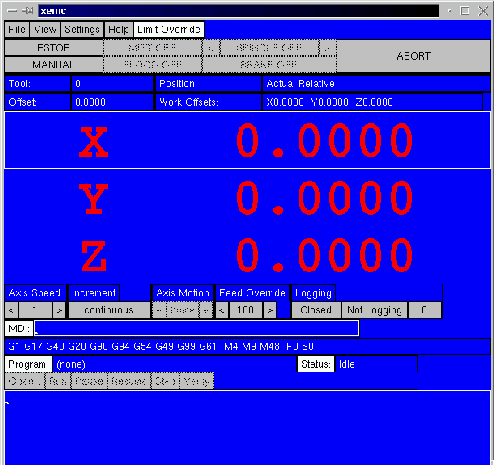 Now
I see xemc with huge red letters.
When I try to bring it out of estop it
won't. I press file and slide down
to quit and release the mouse button. A
dialog pops up quit? Yes! And xemc and
EMC go away.
Now
I see xemc with huge red letters.
When I try to bring it out of estop it
won't. I press file and slide down
to quit and release the mouse button. A
dialog pops up quit? Yes! And xemc and
EMC go away.
Won't come out of estop. 'eh. Well
what are the possibilities here. (look
in emc.ini) The major sections are
labeled:
1.
EMC
2.
DISPLAY
3.
TASK
4.
RS274NGC
5.
EMCMOT
6.
TRAJ
7.
AXIS_0
8.
AXIS_1
9.
AXIS_2
10.
EMCIO
11.
EMCSERVER
12.
EMCSTRIP
Now the huge red letters are a clue.
They say that the axis limit switches
are tripped. But I don't have any axis
limits hooked up! Well what's happening
here is that EMC is looking at the pins
that the ini says are the limits and
those pins are defined in the ini as
being tripped.
Let's start by looking in the EMCMOT
section for answers. (We did that for
the period problem already.)
[EMCMOT]
; Platform for
motion
PLAT = realtime
; PLAT =
nonrealtime
Yes we want realtime motion so that's
good.
; Name of motion
control program
EMCMOT =
steppermod.o
; EMCMOT =
freqmod.o
; EMCMOT =
stgmod.o
; EMCMOT =
stg8mod.o
; EMCMOT =
emcmotsim
We already know that it's trying to run
steppermod.o. Steppermod and freqmod
both use the parallel port(s) for their
signals so let's look at what we have
defined for the parallel port here with
motion.
; Address for
parallel port used for steppers
PARPORT_IO_ADDRESS
= 0x378
Now I want to know if that is the
address that my machine's parallel port
is registered to so I look in the Kmenu
under settings / information / I/O port
information / in the popup menus for
Mandrake 7. Yours may be
different!
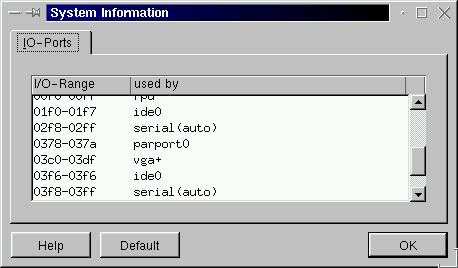
And sure enough, parallel port 0 is
using an address that begins with
0x378. Now what do I
do. Well first I need to
find out which of the parallel port pins
is used for those limits. For this
I can just look in the software page
from NIST. They ship it with the
release.tgz in the emc/doc
directory. It doesn't have the
pictures but the text is enough for me
here.
Setting up
Stepper Motors (from the nist page)
Currently the
EMC supports stepper motors with a 2-bit
step-and-direction interface, with bits
mapped to the parallel port. Each
parallel port has 12 bits
of output and 5 bits of input. The
outputs are used to drive the step and
direction of each motor. 12 bits of
output mean that up to 6 stepper
motorscan be controlled. The inputs can
be used to detect limit or home switch
trips. 5 bits of input mean that only
one axes can get full positive,
negative,and home switch inputs. The EMC
mapping compromises for 3 axes of
stepper motor control, with all positive
limit switches being mapped to one
input, all
negative limit switches being mapped to
another input, and all home switches
being mapped to a third input. Other
permutations are possible, of
course, and can be changed in the
software. You could also add 2
additional parallel ports (LPT2, LPT3),
and get 36 bits of output and 15 bits
ofinput. Some parallel ports also let
you take 4 outputs and use them as
inputs, for 8 outputs and 9 inputs for
each parallel port. This would let you
get 3 axes
of control and full switch input per
parallel port. See Using the PC parallel
port for digital I/O for more
information on the parallel port.
The pinout for
the EMC stepper motor interface is as
follows:
Output
Parallel Port
------
-------------
X
direction D0, pin 2
X
clock
D1, pin 3
Y
direction D2, pin 4
Y
clock
D3, pin 5
Z
direction D4, pin 6
Z
clock
D5, pin 7
Input
Parallel Port
-----
-------------
X/Y/Z
lim + S3, pin 15
X/Y/Z
lim - S4, pin 13
X/Y/Z
home S5, pin 12
Stepper motor
control is implemented using a second
real-time task that runs at 100
microseconds. This task writes the
parallel port output with bits set
or cleared based on whether the pulse
should be raised or lowered. This gives
an effective period of 200 microseconds
for a full up-and-down pulse,
or a frequency limited to about 5
kilohertz.
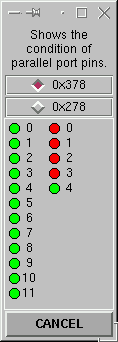
Well now I know that EMC is looking for
all of the + limits on pin 15 - signal
S3, the - limits on pin 13 - S4, and the
home signals on pin 12 - S5. So what's
happening at that parport address.
Well there are several ways to find
out. The one that I like
personally is a little Tcl/Tk script
that is available from the linuxCNC.org/dropbox.
It's called ioshow.tcl. The
direction signals are easy to see but
the stepper clock pulses only show once
in a while.
You can use this from the scripts
menu in tkemc, if you have a scripts
menu with your release, while emc
is running and see some of what's
happening. If you don't have
a scripts menu, you may run it from a
terminal and see what the pins are
doing. In a new console
window enter:
[root@localhost
ray]# cd /usr/local/nist/emc
[root@localhost
emc]# scripts/IO_Show.tcl
The left column of pins are the D
signals. The right column are the
S signals. The right
hand column begins with S3 so the first
led shows that signal S3 is high.
If you want further information about
the parallel port I suggest the
following references.
http://www.isd.mel.nist.gov/projects/emc/parport.html
http://206.19.206.56/parallel.htm
The first is a good technical reference
that will explain how the state of the
individual pin is created and
interpreted in the various incarnations
of the parallel port. The second
is a good basic introduction to wiring
the parallel port so that it works for
you.
Now I know that the EMC thinks that
switches are closed to the limits and
the home pins because the signals are
high. Now I'm ready to look in the
ini file again. This time I'm
going to look in each of the axis
sections because it is there that the
state of the individual signals are set.
;
First axis
[AXIS_0]
TYPE
=
LINEAR
UNITS
=
0.03937007874016
HOME
=
0.000
MAX_VELOCITY
=
1.2
P
= 1000.000
I
= 0.000
D
= 0.000
FF0
= 0.000
FF1
= 0.000
FF2
= 0.000
BACKLASH
= 0.000
BIAS
= 0.000
MAX_ERROR
= 0.000
DEADBAND
= 0.000
CYCLE_TIME
=
0.001000
INPUT_SCALE
=
1000 0
OUTPUT_SCALE
= 1.000 0.000
MIN_LIMIT
=
-10.0
MAX_LIMIT
=
10.0
MIN_OUTPUT
=
-10
MAX_OUTPUT
=
10
FERROR
= 1.000
MIN_FERROR
= 0.010
HOMING_VEL
=
0.1
HOME_OFFSET
=
0.0
ENABLE_POLARITY
=
0
MIN_LIMIT_SWITCH_POLARITY
= 1
MAX_LIMIT_SWITCH_POLARITY
= 1
HOME_SWITCH_POLARITY
=
1
HOMING_POLARITY
=
1
JOGGING_POLARITY
=
1
FAULT_POLARITY
=
1
;
Parameters for Inland Motor BMHS-0701 X
20
TORQUE_UNITS
=
OZ_IN
ARMATURE_RESISTANCE
=
1.10
ARMATURE_INDUCTANCE
=
0.0120
BACK_EMF_CONSTANT
=
0.0254
ROTOR_INERTIA
=
0.0104
DAMPING_FRICTION_COEFFICIENT
= 0.083
SHAFT_OFFSET
=
0
REVS_PER_UNIT
=
10
;
Parameters for generic amplifier
AMPLIFIER_GAIN
=
1
MAX_OUTPUT_CURRENT
=
10
LOAD_RESISTANCE
=
1
;
parameters for generic encoder
COUNTS_PER_REV
=
4096
I highlighted the three lines that
really count for what I'm trying to do
here. These are S4, S3, and
S5 in roughly that order. Now we
want the computer to think that the
limit switches are open and the home
switch is closed. That way it will
home as soon as we press the home
button. And it will never hit a
hard limit. I should caution you
that you don't want to run a real
machine this way, at least not for long.
So I changed the settings of these to
the lines shown below.
MIN_LIMIT_SWITCH_POLARITY
= 0
MAX_LIMIT_SWITCH_POLARITY
= 0
HOME_SWITCH_POLARITY
=
1
And I did it for the other two axis as
well. Then I saved the file and
started EMC again.
This time xemc came up with giant
yellow letters. Trust me, this is
an improvement. It means that each
EMC axis has not been homed . But
at least they are not sitting on limit
switches like they were before.
But EMC will still not come out of estop
so we need to look further into the
definitions within the ini file.
What else is there that would affect
estop. Well there is a pin
somewhere that looks at external estop
because many machines use an external
switch to turn off the power to motors
when estop is required. Rather
than the computer turning off power to
drives, the computer is notified that
power has been shut off to the
drives. That way the computer can
switch itself into estop state when that
state exists for the machine tool.
You may have noticed that this
condition is not defined for the
parallel port that NIST listed
above. There is no estop in.
So when we are using that parallel port
definition, this should not be a
problem. So what parallel port
definition are we using with the stock
emc.ini.
;
section for main IO controller
parameters
-----------------------------------
[EMCIO]
;
Platform for IO controller
PLAT
=
nonrealtime
;
Name of IO controller program, e.g.,
bridgeportio
EMCIO
=
bridgeportio
;
EMCIO
=
minimillio
;
EMCIO
=
simio
;
cycle time, in seconds
CYCLE_TIME
= 0.100
;
tool table file
TOOL_TABLE
= emc.tbl
;
address for parallel port used for
auxiliary IO
PARPORT_IO_ADDRESS
= 0x278
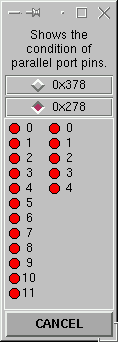 Aha!
Auxiliary I/O uses a parallel port at
0x278. Now you may not know this,
but the bridgeportio system uses the
auxiliary I/O port for some of its
functions. Stuff like mist or
flood coolant, spindle speed and
direction, and estop state.
So let's use ioshow again to see
what the state of these addresses are
for my computer. (I don't have a
parallel port installed at this address)
Aha!
Auxiliary I/O uses a parallel port at
0x278. Now you may not know this,
but the bridgeportio system uses the
auxiliary I/O port for some of its
functions. Stuff like mist or
flood coolant, spindle speed and
direction, and estop state.
So let's use ioshow again to see
what the state of these addresses are
for my computer. (I don't have a
parallel port installed at this address)
Everything at that address is set
high. Now rather than figuring out
the rest of what the I/O section of the
idi file is trying to tell me, I'll just
switch definitions of the I/O
system. I can do this by changing
one line.
;
Name of IO controller program, e.g.,
bridgeportio
EMCIO
=
bridgeportio
;
EMCIO
=
minimillio
;
EMCIO
=
simio
I comment out the
bridgeportio line and uncomment the
minimillio line. The result looks
like this.
;
Name of IO controller program, e.g.,
bridgeportio
;
EMCIO
=
bridgeportio
EMCIO
=
minimillio
;
EMCIO
=
simio
After I save my
latest change, I'm ready to try running
EMC again. And now I can get have
green letters after I press <estop
off> and <machine on>. Then
with EMC still in manual mode, I clicked
on the home button below the big numbers
and x turned green, click on the y
numbers or press y on the keyboard and
clicked home again and y turned
green. Repeated it for z and EMC
is homed out and ready to work for me.
Your success may vary. It
depends upon the version of emc.ini that
is shipped with your release. It
also depends upon the parallel port
definitions that your machine is using
and the way its parallel port hardware
sets up the address values. You
can click here to view my edited emc.ini.
You are also welcome to save it and use
it for your system.
Now at least you know how I did it.
Good luck
This page is maintained by Ray
Henry. I'd like to hear your
comments and suggestions concerning
it. Send email to rehenry@up.net.
This guide is
free; you can redistribute it and/or
modify
it under the terms of
the GNU General Public License as
published by
the Free Software
Foundation; either version 2 of the
License, or
(at your option) any
later version.
(C) Ray Henry 2000

 Now
I see xemc with huge red letters.
When I try to bring it out of estop it
won't. I press file and slide down
to quit and release the mouse button. A
dialog pops up quit? Yes! And xemc and
EMC go away.
Now
I see xemc with huge red letters.
When I try to bring it out of estop it
won't. I press file and slide down
to quit and release the mouse button. A
dialog pops up quit? Yes! And xemc and
EMC go away.
 Aha!
Auxiliary I/O uses a parallel port at
0x278. Now you may not know this,
but the bridgeportio system uses the
auxiliary I/O port for some of its
functions. Stuff like mist or
flood coolant, spindle speed and
direction, and estop state.
So let's use ioshow again to see
what the state of these addresses are
for my computer. (I don't have a
parallel port installed at this address)
Aha!
Auxiliary I/O uses a parallel port at
0x278. Now you may not know this,
but the bridgeportio system uses the
auxiliary I/O port for some of its
functions. Stuff like mist or
flood coolant, spindle speed and
direction, and estop state.
So let's use ioshow again to see
what the state of these addresses are
for my computer. (I don't have a
parallel port installed at this address)